How Do You Know What J Variable Is for F Test
Contents :
- What is an F Statistic?
- The F Statistic and P Value
- In ANOVA
- In Regression
- F Distribution
- F Dist on the TI 89
- Using the F Statistic Tabular array
See also: What is an F-Test?
What is an F Statistic?
Image: U of Michigan.
Scout the video for an overview:
Tin can't see the video? Click here.
An F statistic is a value y'all get when you run an ANOVA exam or a regression assay to find out if the means between ii populations are significantly dissimilar. It's like to a T statistic from a T-Test; A T-test will tell you if a single variable is statistically significant and an F examination volition tell you lot if a group of variables are jointly significant.
What is "Statistically Significant"?
Simply put, if you have significant upshot, it means that your results likely did not happen by chance. If yous don't accept statistically significant results, you throw your exam data out (equally it doesn't show anything!); in other words, you tin't reject the null hypothesis.
Using The F Statistic.
You can employ the F statistic when deciding to support or reject the null hypothesis. In your F exam results, you'll have both an F value and an F critical value.
In general, if your calculated F value in a exam is larger than your F critical value, you can reject the null hypothesis. However, the statistic is just one measure of significance in an F Test. You should too consider the p value. The p value is determined by the F statistic and is the probability your results could accept happened past chance.
Back to Elevation
The F Statistic and P Value
The F statistic must be used in combination with the p value when you are deciding if your overall results are significant. Why? If you lot accept a significant event, information technology doesn't mean that all your variables are meaning. The statistic is only comparing the joint effect of all the variables together.
For example, if you are using the F Statistic in regression assay (perhaps for a change in R Squared, the Coefficient of Determination), yous would apply the p value to get the "big moving picture."
- If the p value is less than the alpha level, go to Footstep 2 (otherwise your results are not significant and you cannot refuse the null hypothesis). A common alpha level for tests is 0.05.
- Study the private p values to find out which of the individual variables are statistically significant.
Back to Tiptop
The F Value in ANOVA
The F value in one way ANOVA is a tool to help you answer the question "Is the variance between the means of two populations significantly different?" The F value in the ANOVA test also determines the P value; The P value is the probability of getting a result at least equally extreme as the 1 that was actually observed, given that the aught hypothesis is true.
The p value is a probability, while the f ratio is a exam statistic, calculated as:
F value = variance of the group means (Mean Foursquare Betwixt) / hateful of the within group variances (Mean Squared Fault)
When Do I Reject the Null Hypothesis?
Pass up the null when your p value is smaller than your alpha level. You should non turn down the null if your critical f value is smaller than your F Value, unless you also take a small p-value.
Where this could get confusing is where one of these values seems to indicate that you should reject the nil hypothesis and one of the values indicates you should not. For example, allow'due south say your One Way ANOVA has a p value of 0.68 and an blastoff level of 0.05. As the p value is large, you should not reject the nil hypothesis. However, your f value is 4.0 with an f critical value of 3.2. Should yous now reject the null hypothesis? The answer is NO.
Why?
The F value should ever be used along with the p value in deciding whether your results are pregnant enough to pass up the zip hypothesis. If you become a large f value (one that is bigger than the F critical value found in a tabular array), it means something is pregnant, while a pocket-sized p value means all your results are significant. The F statistic just compares the joint event of all the variables together. To put it simply, turn down the nix hypothesis only if your blastoff level is larger than your p value.
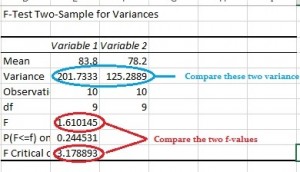
Caution: If y'all are running an F Test in Excel, make sure your variance 1 is smaller than variance 2. This "quirk" can requite you lot an wrong f ratio if you put the variances in the wrong place. Come across the bottom of this article for an example: F Test Ii Sample Variances in Excel.
Back to Top
F Value in Regression
The F value in regression is the result of a examination where the null hypothesis is that all of the regression coefficients are equal to nothing. In other words, the model has no predictive capability. Basically, the f-exam compares your model with nada predictor variables (the intercept merely model), and decides whether your added coefficients improved the model. If you become a significant result, then whatever coefficients you included in your model improved the model's fit.
Read your p-value starting time. If the p-value is small (less than your alpha level), you can decline the nix hypothesis. Only and so should you lot consider the f-value. If y'all don't reject the null, ignore the f-value.
Many authors recommend ignoring the P values for individual regression coefficients if the overall F ratio is not statistically significant. This is because of the multiple testing problem. In other words, your p-value and f-value should both be statistically pregnant in gild to correctly interpret the results.
If you want to know whether your regression F-value is significant, you'll need to find the critical value in the f-table. For example, permit's say you had 3 regression degrees of liberty (df1) and 120 residual degrees of freedom (df2). An F statistic of at least 3.95 is needed to reject the null hypothesis at an alpha level of 0.1. At this level, you stand up a i% chance of being incorrect (Archdeacon, 1994, p.168). For more than details on how to do this, see: F Examination. F Values will range from 0 to an arbitrarily large number.
Back to Top
F Distribution
The F Distribution is a probability distribution of the F Statistic. In other words, it'southward a distribution of all possible values of the f statistic.
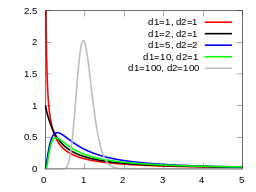
F Distribution.
The distribution is an asymmetric distribution usually used for ANOVA . It has a minimum value of nada; there is no maximum value. The distribution'due south peak happens just to the right of zero and the higher the f-value after that point, the lower the bend. The F distribution is actually a drove of distribution curves. The F distribution is related to chi-square, because the f distribution is the ratio of ii chi-square distributions with degrees of freedom ν1 and ν2 (note: each chi-square is first been divided past its degrees of freedom). Each curve depends on the degrees of liberty in the numerator (dfn) and the denominator (dfd). These depend upon your sample characteristics.
For example, in a unproblematic one-fashion ANOVA betwixt-groups,
- Dfn = a – 1
- dfd = Northward – a
where:
- a = the number of groups
- north = the total number of subjects in the experiment
The degrees of liberty in the denominator (dfd) is besides referred to as the degrees of freedom mistake (dfe).
The F Distribution is also called the Snedecor'due south F, Fisher'south F or the Fisher–Snedecor distribution.
Back to Acme
F Distribution on the TI 89: Overview
There are two types of primary problem you lot'll encounter with the F-Distribution you might be asked to find the area under a F curve given numerator degrees of freedom (ndf), denominator degrees of freedom (ddf), and a sure range (for example, P( 1 ≤ 10 ≤ ii ), or you might be asked to find the F value with expanse to the left, a sure ndf and ddf (useful for finding critical values for hypotheses tests).
F Distribution on TI 89: Steps
Example trouble: find the area under a F bend with numerator degrees of freedom (ndf) 4 and
denominator degrees of freedom (ddf) 10 for For, P( 1≤ X ≤ 2 ):
Step one: Press APPS.
Step 2: Press ENTER twice to go to the list entry screen.
Stride three: Press F5 for "F5-Distr."
Step 4: Scroll down to "A:F Cdf" and press ENTER.
Step 5: Enter one in the box for "Lower Value," then press the downward arrow cardinal.
Step half-dozen: Enter ii in the box for "Upper Value," then press the down arrow key.
Step 7: Enter four in the "Num df" box, then press the down arrow key.
Step eight: Enter v in the "Den df" box.
Stride 9: Press ENTER. The reckoner volition render .281 as the answer.
Example problem: to find the F value with surface area to the left, with ndf = 5, ddf = eight, and an area of .99:
Stride 1: Press APPS.
Step 2: Press ENTER twice to get to the listing entry screen.
Step 3: Printing F5 for "F5-Distr."
Footstep four: Printing 2 for "Inverse."
Step v: Press four for "Changed F…," then press ENTER.
Pace 6: Enter .99 in the "Area" box, and so press the down arrow key.
Footstep 7: Enter five in the "Num df," box, then printing the down arrow central.
Pace 8: Enter 8 in the "Den df." box, then press ENTER. This returns the answer (63183).
Tip: For P( X ≥ one ), enter i in the box for Lower Value and ten ^ 99 in the box for
Upper Value, and for For P( 10 ≤ 1 ), enter 0 in the box for Lower Value, and so enter 1 in the box for Upper
Value.
Lost your guidebook? You can download one from the TI website here.
Back to Meridian
The F Statistic Table
The F Tabular array is a collection of tables that give you the probability for a sure alpha level. The F Tabular array is actually a collection of tables, for four alpha levels: .10. .five, .025 and .01.
The three f tables y'all can find on this site are for alpha levels of .10, .0 and .01. When using the F dist. table, always put the numerator degrees of freedom first; if you switch the numerator and denominator around, you'll go a different result. The table gives you the area in the correct tail. Instead of a table, you can use a estimator — which will give you more accurate results.
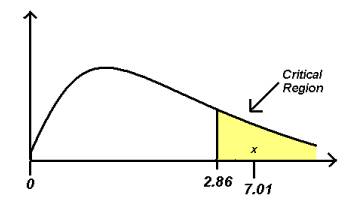
What is the F Statistic Table Used for?
When you lot have establish the F value, you tin can compare it with an f critical value in the table. If your observed value of F is larger than the value in the F table, and so yous can reject the nada hypothesis with 95 percent confidence that the variance between your ii populations isn't due to random chance.
How to employ the F Statistic Table
Watch the video for an overview:
How to read an F table in statistics
Tin't run across the video? Click hither.
The F Statistic Table is actually a drove of tables. Which specific table y'all utilize will depend on which blastoff level you apply. For example, if you have an blastoff level of .05, and then your correct tail area is .05 (5 pct), and you'll look up the f critical value in the blastoff level = .05 table. The rows in the F Distribution Table represent denominator degrees of freedom and the columns represent numerator degrees of liberty.
For instance, to determine the .ten f disquisitional value for an F distribution with 6 and half-dozen degrees of liberty, expect in the vi cavalcade (numerator) and the half-dozen row (denominator) of the F Table for alpha=.10. F(.10, 6, half dozen) = three.054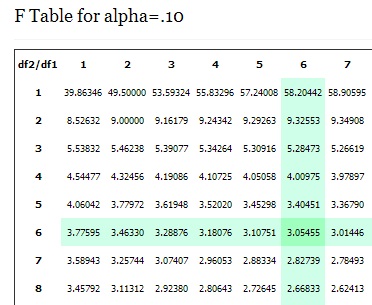 55.
55.
Why Use the F Statistic Tabular array? Why not just use a reckoner?
A calculator will certainly requite yous a fast answer. But with many scenarios in statistics, you lot will look at a range of possibilities and a tabular array is much better for visualizing a large number of probabilities at the aforementioned time.
Back to Top
References
Archdeacon, T. (1994). Correlation and Regression Analysis: A Historian's Guide. Univ of Wisconsin Printing.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Need help with a homework or examination question? With Chegg Report, you tin get footstep-past-footstep solutions to your questions from an expert in the field. Your beginning 30 minutes with a Chegg tutor is free!
Comments? Need to post a correction? Please post a comment on our Facebook page .
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/f-statistic-value-test/
0 Response to "How Do You Know What J Variable Is for F Test"
Post a Comment